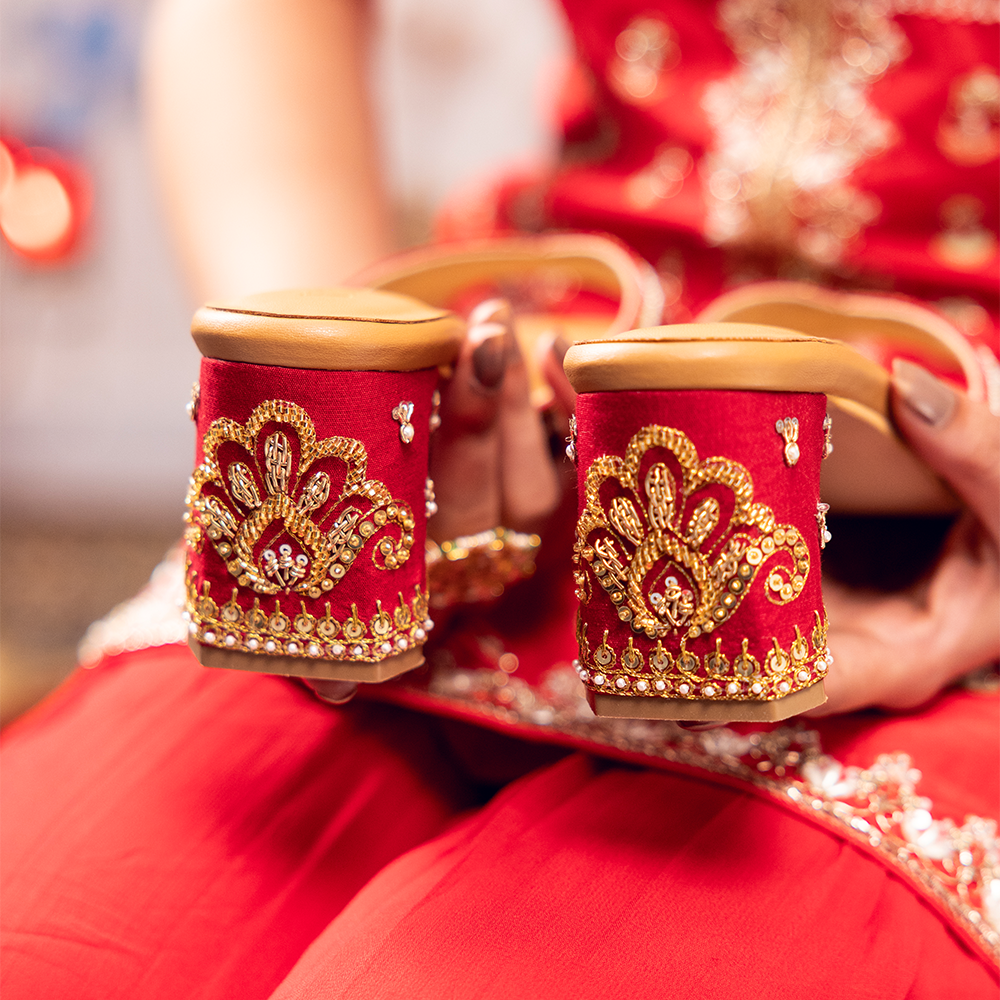
Juttis are a type of traditional Indian footwear that are known for their intricate embroidery and embellishments. The making of juttis is a highly skilled craft that requires a great deal of attention to detail and precision. In this blog, we will delve into the craftsmanship of juttis and explore the techniques that are used to create these beautiful shoes.
Design and Pattern Making
The first step in the making of juttis is the design and pattern making. The design is drawn onto a piece of paper, and then transferred onto the leather or fabric that will be used to make the jutti. The pattern is then cut out, and the pieces are sewn together to create the basic shape of the jutti.
Embroidery and Embellishments
Once the basic shape of the jutti has been created, the embroidery and embellishments are added. The embroidery is often done by hand using a needle and thread, and can feature intricate patterns and designs. Common embroidery styles used on juttis include the popular Phulkari embroidery, Zardozi embroidery, and Gota Patti work.
In addition to embroidery, juttis can also feature other embellishments such as sequins, beads, mirrors, and tassels. These embellishments are often added by hand and require a great deal of skill and patience to create.
Stitching and Finishing
Once the embroidery and embellishments have been added, the jutti is stitched together using a special stitching technique called "Mochi stitch." This stitch is done by hand and involves sewing the upper part of the jutti to the sole using a thick thread. This stitch is not only strong and durable but also adds a decorative element to the jutti.
Finally, the jutti is finished with a leather or fabric lining, and the sole is reinforced with a layer of rubber to make it more durable and slip-resistant.
From the design and pattern making to the embroidery and embellishments, every step of the process is done by hand with a great deal of skill and care. The end result is a beautiful and unique shoe that is not only stylish but also a true work of art.